Interface 명세로 알아보는 Servlet
참고 자료
서블릿이란?
A servlet is a Java programming language class that is used to extend the capabilities of servers that host applications accessed by means of a request-response programming model. Although servlets can respond to any type of request, they are commonly used to extend the applications hosted by web servers. For such applications, Java Servlet technology defines HTTP-specific servlet classes.
Java 에서 HTTP 통신을 활용한 기능을 만들기 위한 클래스이다.
실제로는 아래와 같은 인터페이스로 명시되어 있으며, 구현체가 따로 존재한다.
또한 서블릿은 서블릿 컨테이너에 의해 관리된다.
서블릿 컨테이너가 관리하는 서블릿의 생명주기
1. 서블릿의 인스턴스가 존재하지 않을 때
서블릿 클래스를 로딩한다.
서블릿 클래스의 인스턴스를 생성한다.
서블릿 클래스의 인스턴스를 init() 하여 서블릿을 초기화 한다.
2. Service 메서드가 수행됨으로써, 서블릿에서 수행할 메서드를 수행한다 (요청과 응답)
GET, POST, DELETE, PUT 등 HTTP 메서드를 매핑하는 코드가 구현체로 작성되어 있다.
아래 코드를 자세히 살펴보면 보인다!!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
private void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince;
try {
ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
// Invalid date header - proceed as if none was set
ifModifiedSince = -1;
}
if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp);
} else {
//
// Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever
// method was requested, anywhere on this server.
//
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
3. 서블릿이 사용되지 않을 때 GC 에 의해 메모리 해제가 진행된다.
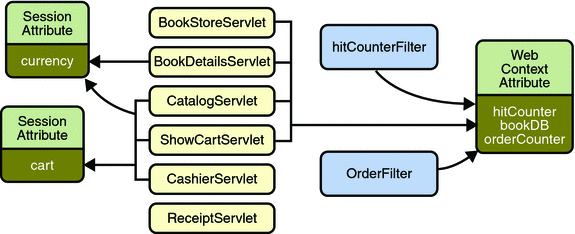
서블릿 컨테이너가 관리하는 서블릿의 멀티쓰레딩
여러 개의 Web Component가 Web Context 에 저장된 객체에 접근 가능하다.
여러 개의 Web Component 가 Session 에 저장된 객체에 접근 가능하다.
Web Context(Servlet Container) 가 멀티 쓰레드를 가졌기 때문에 여러개의 요청을 동시에 처리할 수 있게 되는 것이다.
들어가기 전에
우리가 사용하는 Spring 에서는, MVC 패턴에서 확장된 RestController 가 주로 사용된다.
이때 서버에 요청을 보내고, 서버에서 응답을 해줄때 서블릿이 사용되는데
위 그림과 같이, 필터 -> 디스패처 서블릿 -> 인터셉터 -> 컨트롤러 순으로 처리된다.
즉, Spring 기반 환경에서는 디스패처 서블릿이 사용된다.
Servlet.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public interface Servlet {
void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException;
public ServletConfig getServletConfig();
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException;
public String getServletInfo();
Servlet 인터페이스의 각 메서드들의 명세를 살펴보겠다.
서블릿, 인터페이스 명세로 알아보기
Servlet - 초기화
public void init(ServletConfig config)
Called by the servlet container to indicate to a servlet that the servlet is being placed into service.
The servlet container calls the init method exactly once after instantiating the servlet. The init method must complete successfully before the servlet can receive any requests.
The servlet container cannot place the servlet into service if the init method
Throws a ServletException Does not return within a time period defined by the Web server
Parameter: config – a ServletConfig object containing the servlet’s configuration and initialization parameters
Throws: ServletException – if an exception has occurred that interferes with the servlet’s normal operation
1
2
3
서블릿을 애플리케이션에 등록하겠다고 하는 메서드이다. 서블릿 인스턴스가 생성되면 딱 한 번 수행되는 메서드이다.
매개변수인 ServletConfig 타입의 config 는, 서블릿의 구성과 초기화 정보를 담고 있다.
Servlet - 설정 값 Get
public ServletConfig getServletConfig()
Returns a ServletConfig object, which contains initialization and startup parameters for this servlet.
The ServletConfig object returned is the one passed to the init method.
Implementations of this interface are responsible for storing the ServletConfig object so that this method can return it. The GenericServlet class, which implements this interface, already does this.
1
Servlet 설정을 반환하는 메서드이다.
Servlet - 요청/응답 허가
void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
Called by the servlet container to allow the servlet to respond to a request.
This method is only called after the servlet’s init() method has completed successfully.
The status code of the response always should be set for a servlet that throws or sends an error.
Servlets typically run inside multithreaded servlet containers that can handle multiple requests concurrently. Developers must be aware to synchronize access to any shared resources such as files, network connections, and as well as the servlet’s class and instance variables. More information on multithreaded programming in Java is available in the Java tutorial on multi-threaded programming.
1
2
3
4
5
서블릿 컨테이너에 의해 호출되는 메서드이며, 서블릿에 요청과 응답에 대한 요청을 허가하기 위해 사용**된다.
무조건 서블릿의 init() 메서드가 이전에 호출되어야 사용될 수 있으며,
이때 사용되는 서블릿은 여러 요청을 동시에 수행할 수 있는 다중 스레드 특징을 가지고 있다.
Servlet - 서블릿 정보 확인
public String getServletInfo()
Returns information about the servlet, such as author, version, and copyright.
The string that this method returns should be plain text and not markup of any kind (such as HTML, XML, etc.).
1
서블릿의 작성자, 버전, 저작권 등 서블릿에 대한 정보를 문자열로 반환한다.
Servlet - 서블릿 제거
public void destory()
Called by the servlet container to indicate to a servlet that the servlet is being taken out of service. This method is only called once all threads within the servlet’s service method have exited or after a timeout period has passed.
After the servlet container calls this method, it will not call the service method again on this servlet.
This method gives the servlet an opportunity to clean up any resources that are being held (for example, memory, file handles, threads) and make sure that any persistent state is synchronized with the servlet’s current state in memory.
1
2
3
4
5
서블릿 컨테이너에 의해 실행되는 메서드이며, 더 이상 해당 서블릿을 사용하지 않겠다는 표시로 사용된다.
이 메서드가 최종적으로 완료되는 시점은, 서블릿의 서비스 메서드의 모든 스레드가 종료되거나, 타임아웃이 된 시점이다.
서블릿이 사용하고 있던 모든 리소스를 반환하며 현재 메모리에 있는 서블릿과 동기화를 수행한다. (메모리, 파일 핸들, 스레드)
ServletConfig, 인터페이스 명세로 알아보기
ServletConfig.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public interface ServletConfig {
String getServletName();
public ServletContext getServletContext();
public String getInitParameter(String name);
public Enumeration<String> getInitPa
서블릿 설정 - 서블릿 인스턴스의 이름 Get
public String getServletName()
Returns the name of this servlet instance. The name may be provided via server administration, assigned in the web application deployment descriptor, or for an unregistered (and thus unnamed) servlet instance it will be the servlet’s class name.
the name of the servlet instance
1
해당 서블릿 인스턴스의 이름을 반환한다.
서블릿 설정 - 서블릿 컨텍스트 반환
public ServletContext getServletContext()
Returns a reference to the ServletContext in which the caller is executing.
a ServletContext object, used by the caller to interact with its servlet container
1
해당 서블릿 인스턴스가 관리되어지는 서블릿 컨텍스트를 반환한다.
서블릿 설정 - 서블릿 인스턴스의 이름을 가져오기
public String getInitParameter(String name)
Returns a String containing the value of the named initialization parameter, or null if the parameter does not exist.
name – a String specifying the name of the initialization parameter
a String containing the value of the initialization parameter
1
init 메서드로 초기화된 서블릿 인스턴스의 이름을 가져온다. (어떤 이름으로 서블릿 인스턴스가 생성 되었는지)
서블릿 설정 - 서블릿 인스턴스의 이름을 가져오기 (열거형)
public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames()
Returns the names of the servlet’s initialization parameters as an Enumeration of String objects, or an empty Enumeration if the servlet has no initialization parameters.
an Enumeration of String objects containing the names of the servlet’s initialization parameters
1
getInitParameter() 메서드와 기능은 거의 같다. 다만 열거형으로 반환한다.
ServletRequest, 인터페이스 명세로 알아보기
ServletRequest.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
public Object getAttribute(String name);
public Enumeration<String> getAttributeNames();
public String getCharacterEncoding();
public void setCharacterEncoding(String env)
throws java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public int getContentLength();
public long getContentLengthLong();
public String getContentType();
public ServletInputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
public String getParameter(String name);
public Enumeration<String> getParameterNames();
public String[] getParameterValues(String name);
public Map<String, String[]> getParameterMap();
public String getProtocol();
public String getScheme();
public String getServerName();
public int getServerPort();
public BufferedReader getReader() throws IOException;
public String getRemoteAddr();
public String getRemoteHost();
public void setAttribute(String name, Object o);
public void removeAttribute(String name);
public Locale getLocale();
public Enumeration<Locale> getLocales();
public boolean isSecure();
public RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(String path);
@Deprecated
public String getRealPath(String path);
public int getRemotePort();
public String getLocalName();
public String getLocalAddr();
public int getLocalPort();
public ServletContext getServletContext();
public AsyncContext startAsync() throws IllegalStateException;
public AsyncContext startAsync(ServletRequest servletRequest,
ServletResponse servletResponse) throws IllegalStateException;
public boolean isAsyncStarted();
public boolean isAsyncSupported();
public AsyncContext getAsyncContext();
public DispatcherType getDispatcherType();
서블릿 요청 - 속성에 대한 객체 가져오기
public Object getAttribute(String name)
Returns the value of the named attribute as an Object, or null if no attribute of the given name exists.
Attributes can be set two ways. The servlet container may set attributes to make available custom information about a request. For example, for requests made using HTTPS, the attribute javax.servlet.request.X509Certificate can be used to retrieve information on the certificate of the client. Attributes can also be set programmatically using setAttribute. This allows information to be embedded into a request before a RequestDispatcher call.
Attribute names should follow the same conventions as package names. Names beginning with java.* and javax.* are reserved for use by the Servlet specification. Names beginning with sun., com.sun., oracle.* and com.oracle.*) are reserved for use by Oracle Corporation.
name – a String specifying the name of the attribute
an Object containing the value of the attribute, or null if the attribute does not exist
1
2
3
명명된 속성의 값을 Object로 반환하거나 지정된 이름의 속성이 없으면 null을 반환한다.
즉, 파라미터에 해당하는 서블릿의 속성 이름을 찾아 Object 타입으로 반환한다.
서블릿 요청 - 속성에 대한 객체 가져오기 (열거형)
public Enumeration<String> getAttributeNames()
Returns an Enumeration containing the names of the attributes available to this request. This method returns an empty Enumeration if the request has no attributes available to it.
an Enumeration of strings containing the names of the request’s attributes
1
2
3
이 요청에 사용할 수 있는 속성의 이름을 포함하는 열거형을 반환한다.
이 메서드는 요청에 사용할 수 있는 속성이 없는 경우 빈 열거형을 반환한다.
서블릿 요청 - 인코딩 이름을 GET
public String getCharacterEncoding()
Returns the name of the character encoding used in the body of this request.
This method returns null if the no character encoding has been specified.
The following priority order is used to determine the specified encoding: per request
web application default via the deployment descriptor or ServletContext.setRequestCharacterEncoding(String)
container default via container specific configuration
1
요청에 사용된 문자열 인코딩 이름을 반환한다. 문자열 인코딩이 지정되지 않은 경우에는 null을 반환한다.
서블릿 요청 - 인코딩 이름을 GET
public void getCharacterEncoding(String env)
Overrides the name of the character encoding used in the body of this request.
This method must be called prior to reading request parameters or reading input using getReader().
env – a String containing the name of the character encoding.
1
요청에 사용된 문자열 인코딩 방식을 재 지정한다. 매개변수에는 인코딩 방식을 문자열 타입으로 넣어준다.
서블릿 요청 - 요청 길이 GET
public int getContentLength()
Returns the length, in bytes, of the request body and made available by the input stream, or -1 if the length is not known. For HTTP servlets, same as the value of the CGI variable CONTENT_LENGTH.
an integer containing the length of the request body or -1 if the length is not known or is greater than Integer.MAX_VALUE
1
들어온 요청의 길이를 바이트 단위로 가져온다. HTTP Servlet의 경우에는, CGI 변수 CONTENT_LENGTH와 같다.
서블릿 요청 - 요청 길이 GET (Return type is long)
public long getContentLengthLong()
Returns the length, in bytes, of the request body and made available by the input stream, or -1 if the length is not known. For HTTP servlets, same as the value of the CGI variable CONTENT_LENGTH.
1
들어온 요청의 길이를 바이트 단위로 가져온다. 이 메서드는 long 타입으로 반환한다. 마찬가지로 HTTP Servlet의 경우에는, CGI 변수 CONTENT_LENGTH와 같다.
서블릿 요청 - ContentType Get
public String getContentType()
Returns the MIME type of the body of the request, or null if the type is not known. For HTTP servlets, same as the value of the CGI variable CONTENT_TYPE.
a String containing the name of the MIME type of the request, or null if the type is not known
1
들어온 요청의 ContentType을 문자열 타입으로 가져온다. HttpServlet의 경우 CGI변수의 CONTENT_TYPE 의 값과 같다.
서블릿 요청 - Read request body
public ServletInputStream getInputStream()
Retrieves the body of the request as binary data using a ServletInputStream.
Either this method or getReader may be called to read the body, not both.
1
들어온 요청을 binary 데이터로 검색한다. 즉, 들어온 요청의 body 를 읽는 방법이다. getReader() 메서드나 getInputStream() 메서드로 요청의 본문을 읽을 수 있다.
서블릿 요청 - Read request param
public String getParameter(String name)
Returns the value of a request parameter as a String, or null if the parameter does not exist. Request parameters are extra information sent with the request.
For HTTP servlets, parameters are contained in the query string or posted form data.
You should only use this method when you are sure the parameter has only one value. If the parameter might have more than one value, use getParameterValues.
If you use this method with a multivalued parameter, the value returned is equal to the first value in the array returned by getParameterValues.
If the parameter data was sent in the request body, such as occurs with an HTTP POST request, then reading the body directly via getInputStream or getReader can interfere with the execution of this method.
1
2
3
요청에서 파라미터가 1개 일때 사용되는 메서드로, 해당하는 매개변수를 문자열로 반환한다. 만약 매개변수가 없다면 null 을 반환한다.
HTTP Servlet 에서는, 매개변수를 Query String 이나, Form data 를 취급한다.
서블릿 요청 - Read request param (열거형)
public Enumeration<String> getParameterNames()
Returns an Enumeration of String objects containing the names of the parameters contained in this request.
If the request has no parameters, the method returns an empty Enumeration.
1
요청 파라미터를 열거형으로 반환한다.
서블릿 요청 - Read request param (Array)
public String [] getParameterValues(String name)
Returns an array of String objects containing all of the values the given request parameter has, or null if the parameter does not exist.
If the parameter has a single value, the array has a length of 1.
1
요청 파라미터로 들어온 name 에 해당하는 값을 가진 객체를 배열로 반환한다.
서블릿 요청 - Read request param (Array)
public Map<String, String[]> getParameterMap()
Returns a java.util.Map of the parameters of this request. Request parameters are extra information sent with the request.
For HTTP servlets, parameters are contained in the query string or posted form data.
1
2
3
요청 들어온 매개변수를 Map 타입으로 반환한다.
HTTP Servlet 에서는, 매개변수를 Query String 이나, Form data 를 취급한다.
서블릿 요청 - Read protocol
public String getProtocol()
Returns the name and version of the protocol the request uses in the form protocol/majorVersion.minorVersion,
for example, HTTP/1.1. For HTTP servlets, the value returned is the same as the value of the CGI variable SERVER_PROTOCOL.
1
2
3
요청 들어온 프로토콜의 버전을 반환한다. (예시 : HTTP/1.1)
HTTP Servlet 에서는, CGI 변수에 담긴, SERVER_PROTOCOL 값을 반환한다.
서블릿 요청 - Read request scheme (Array)
public String getScheme()
Returns the name of the scheme used to make this request,
for example, http, https, or ftp. Different schemes have different rules for constructing URLs, as noted in RFC 1738.
1
요청 들어온 스키마를 반환한다. (예시 : http, https, ftp ...)
서블릿 요청 - Read request host server name
public String getServerName()
Returns the host name of the server to which the request was sent.
It is the value of the part before “:” in the Host header value, if any, or the resolved server name, or the server IP address.
1
2
3
요청을 처리하고 있는 서버의 host 이름을 반환한다.
서버의 IP 주소 혹은, 도메인 주소
서블릿 요청 - Read request host server port
public int getServerPort()
Returns the port number to which the request was sent.
It is the value of the part after “:” in the Host header value, if any, or the server port where the client connection was accepted on.
1
요청을 처리하고 있는 서버의 포트 번호를 반환한다.
서블릿 요청 - Read request body by BufferedReader
public BufferedReader getReader()
Retrieves the body of the request as character data using a BufferedReader.
The reader translates the character data according to the character encoding used on the body.
Either this method or getInputStream may be called to read the body, not both.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
BufferedReader를 사용하여 요청 body를 문자 데이터로 검색한다.
리더는 본문에 사용된 문자 인코딩에 따라 문자 데이터를 번역하며,
이 메서드 또는 getInputStream 중 하나를 호출하여 body를 읽을 수 있다.
둘 다 호출할 수는 없다.
서블릿 요청 - Read request client Ip Address OR Last Proxy Address
ServletRequest - public String getRemoteAddr()
Returns the Internet Protocol (IP) address of the client or last proxy that sent the request.
For HTTP servlets, same as the value of the CGI variable REMOTE_ADDR.
1
2
3
클라이언트의 IP 주소나, 마지막 프록시 주소를 반환한다.
HTTP Servlet 에서는, CGI 변수의 REMOTE_ADDR 의 값과 같다.
서블릿 요청 - Read request Client IP Address OR REMOTE_HOST
ServletRequest - public String getRemoteHost()
Returns the fully qualified name of the client or the last proxy that sent the request.
If the engine cannot or chooses not to resolve the hostname (to improve performance), this method returns the dotted-string form of the IP address.
For HTTP servlets, same as the value of the CGI variable REMOTE_HOST.
1
2
3
4
5
클라이언트의 Name 혹은 마지막 프록시의 Name을 반환한다.
HTTP Servlet 에서는, CGI 변수의 REMOTE_HOST 와 같다.
만약, 브라우저 엔진이 호스트 이름을 숨기도록 되어있다면, IP 주소를 반환한다.
서블릿 요청 - Set request Attribute
ServletRequest - public void setAttribute(String name, Object o)
Stores an attribute in this request.
Attributes are reset between requests.
This method is most often used in conjunction with RequestDispatcher.
Attribute names should follow the same conventions as package names.
Names beginning with java.* and javax.* are reserved for use by the Servlet specification.
Names beginning with sun., com.sun., oracle.* and com.oracle.*) are reserved for use by Oracle Corporation.
If the object passed in is null, the effect is the same as calling removeAttribute.
It is warned that when the request is dispatched from the servlet resides in a different web application by RequestDispatcher, the object set by this method may not be correctly retrieved in the caller servlet.
1
해당 요청에 대한 속성을 저장한다.
서블릿 요청 - read request Client’s Locale
public Locale getLocale()
Returns the preferred Locale that the client will accept content in, based on the Accept-Language header.
If the client request doesn’t provide an Accept-Language header, this method returns the default locale for the server.
1
클라이언트가 수용할 수 있는 물리적인 지역을 나타내는 Locale 을 반환한다. (Accept-Language Header 를 까보는 것이다.)
서블릿 요청 - read request Client’s Locale (열거형)
public Enumeration<Locale> getLocales()
Returns an Enumeration of Locale objects indicating, in decreasing order starting with the preferred locale, the locales that are acceptable to the client based on the Accept-Language header.
If the client request doesn’t provide an Accept-Language header, this method returns an Enumeration containing one Locale, the default locale for the server.
1
클라이언트가 수용할 수 있는 물리적인 지역을 나타내는 Locale 을 열거형으로 반환한다. (Accept-Language Header 를 까보는 것이다.)
서블릿 요청 - is request secured
public boolean isSecure()
Returns a boolean indicating whether this request was made using a secure channel, such as HTTPS.
1
요청이 HTTPS 와 같이 보안 인증이 되어있는지 여부를 확인한다.
서블릿 요청 - RequestDispatcher 반환
ServletRequest - public RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(String path)
Returns a RequestDispatcher object that acts as a wrapper for the resource located at the given path.
A RequestDispatcher object can be used to forward a request to the resource or to include the resource in a response.
The resource can be dynamic or static.
The pathname specified may be relative, although it cannot extend outside the current servlet context.
If the path begins with a “/” it is interpreted as relative to the current context root.
This method returns null if the servlet container cannot return a RequestDispatcher.
The difference between this method and ServletContext.getRequestDispatcher is that this method can take a relative path.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
지정된 경로에 있는 리소스에 대한 래퍼 역할을 하는 RequestDispatcher 객체를 반환한다.
RequestDispatcher 개체를 사용하여 요청을 리소스에 전달하거나 리소스를 응답에 포함할 수 있다.
리소스는 동적이거나 정적일 수 있다.
지정된 경로 이름은 상대적일 수 있지만 현재 서블릿 컨텍스트 외부로 확장할 수는 없다.
경로가 "/"로 시작하면 현재 컨텍스트 루트에 상대적인 것으로 해석된다.
이 메서드는 서블릿 컨테이너가 RequestDispatcher를 반환할 수 없는 경우 null을 반환.
이 메서드와 ServletContext.getRequestDispatcher의 차이점은 이 메소드가 상대 경로를 사용할 수 있다.
ServletResponse, 인터페이스 명세로 알아보기
ServletResponse.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public interface ServletResponse {
String getCharacterEncoding();
public String getContentType();
public ServletOutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException;
public PrintWriter getWriter() throws IOException;
public void setCharacterEncoding(String charset);
public void setContentLength(int len);
public void setContentLengthLong(long length);
public void setContentType(String type);
public void setBufferSize(int size);
public int getBufferSize();
public void flushBuffer() throws IOException;
public void resetBuffer();
public boolean isCommitt
ServletResponse - public String getCharacterEncoding()
Returns the name of the character encoding (MIME charset) used for the body sent in this response. The charset for the MIME body response can be specified explicitly or implicitly.
The priority order for specifying the response body is:
- explicitly per request using setCharacterEncoding and setContentType
- implicitly per request using setLocale
- per web application via the deployment descriptor or ServletContext.setRequestCharacterEncoding(String)
- container default via vendor specific configuration
- ISO-8859-1
Calls made to setCharacterEncoding, setContentType or setLocale after getWriter has been called or after the response has been committed have no effect on the character encoding.
If no character encoding has been specified, ISO-8859-1 is returned.
See RFC 2047 (http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2047.txt) for more information about character encoding and MIME.
1
응답 문자열 인코딩을 반환한다.
ServletResponse - public String getContentType()
Returns the content type used for the MIME body sent in this response.
The content type proper must have been specified using setContentType before the response is committed.
If no content type has been specified, this method returns null.
If a content type has been specified and a character encoding has been explicitly or implicitly specified as described in getCharacterEncoding, the charset parameter is included in the string returned.
If no character encoding has been specified, the charset parameter is omitted.
1
응답 컨텐츠 타입을 문자열 타입으로 반환한다.
ServletResponse - public ServletOutputStream getOutputStream()
Returns a ServletOutputStream suitable for writing binary data in the response.
The servlet container does not encode the binary data.
Calling flush() on the ServletOutputStream commits the response. Either this method or getWriter may be called to write the body, not both.
1
2
3
4
5
응답 데이터를 binary 로 쓰기가 가능한, 서블릿 출력 스트림 타입으로 반환한다.
서블릿 컨테이너가 binary 데이터로 부호화하지 않는다.
flush() 라는 메서드를 호출하여 동일한 역할을 수행할 수 있지만, 둘 중 하나만 사용해야한다.
ServletResponse - public PrintWriter getWriter()
Returns a PrintWriter object that can send character text to the client.
The PrintWriter uses the character encoding returned by getCharacterEncoding.
If the response’s character encoding has not been specified as described in getCharacterEncoding (i.e., the method just returns the default value ISO-8859-1), getWriter updates it to ISO-8859-1.
1
클라이언트에 응답하기 위해 "응답한다"는 의미를 가진 객체를 가져온다.
ServletResponse - public void setCharacterEncoding(String charset)
Sets the character encoding (MIME charset) of the response being sent to the client,
for example, to UTF-8. If the character encoding has already been set by container default, ServletContext default, setContentType or setLocale, this method overrides it.
Calling setContentType with the String of text/html and calling this method with the String of UTF-8 is equivalent with calling setContentType with the String of text/html; charset=UTF-8.
This method can be called repeatedly to change the character encoding.
This method has no effect if it is called after getWriter has been called or after the response has been committed.
Containers must communicate the character encoding used for the servlet response’s writer to the client if the protocol provides a way for doing so. In the case of HTTP, the character encoding is communicated as part of the Content-Type header for text media types. Note that the character encoding cannot be communicated via HTTP headers if the servlet does not specify a content type; however, it is still used to encode text written via the servlet response’s writer.
1
응답의 문자열 인코딩을 지정한다.
ServletResponse - public void setContentLength(int len)
Sets the length of the content body in the response
In HTTP servlets, this method sets the HTTP Content-Length header.
1
2
3
응답 body의 길이를 지정한다. (정수형)
HTTP Servlet 에서는, HTTP Content-Length 를 지정하는 것과 같다.
ServletResponse - public void setContentLengthLong(long length)
Sets the length of the content body in the response
In HTTP servlets, this method sets the HTTP Content-Length header.
1
2
3
응답 body의 길이를 지정한다. (Long 형)
HTTP Servlet 에서는, HTTP Content-Length 를 지정하는 것과 같다.
ServletResponse - public void setContentType(String type)
Sets the content type of the response being sent to the client, if the response has not been committed yet.
The given content type may include a character encoding specification,
for example, text/html;charset=UTF-8.
The response’s character encoding is only set from the given content type if this method is called before getWriter is called.
This method may be called repeatedly to change content type and character encoding.
This method has no effect if called after the response has been committed.
It does not set the response’s character encoding if it is called after getWriter has been called or after the response has been committed.
Containers must communicate the content type and the character encoding used for the servlet response’s writer to the client if the protocol provides a way for doing so.
In the case of HTTP, the Content-Type header is used.
1
2
3
응답 Content Type 을 지정한다. (예시 : text/html;charset=UTF-8.)
HTTP의 경우, Content-Type 의 헤더를 지정하는 것이다.
ServletResponse - public String setBufferSize(int size)
Sets the preferred buffer size for the body of the response.
The servlet container will use a buffer at least as large as the size requested.
The actual buffer size used can be found using getBufferSize.
A larger buffer allows more content to be written before anything is actually sent, thus providing the servlet with more time to set appropriate status codes and headers.
A smaller buffer decreases server memory load and allows the client to start receiving data more quickly.
This method must be called before any response body content is written; if content has been written or the response object has been committed, this method throws an IllegalStateException.
1
2
3
4
5
응답 body에 대한 기본 버퍼 크기를 설정한다.
서블릿 컨테이너는 매개변수에 들어온 버퍼의 크기를 최소로 잡고 사용한다.
사용된 실제 버퍼 크기는 getBufferSize를 사용하여 찾을 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
버퍼가 클수록 실제로 전송되기 전에 더 많은 내용을 작성할 수 있으므로 서블릿에 적절한 상태 코드와 헤더를 설정할 수 있는 시간이 더 많이 제공된다.
버퍼가 작을수록 서버 메모리 로드가 줄어들고 클라이언트가 데이터 수신을 더 빨리 시작할 수 있다.
이 메소드는 응답 본문 내용이 작성되기 전에 호출되어야 한다.
내용이 작성되었거나 응답 객체가 커밋된 경우 이 메서드는 IllegalStateException 예외를 던진다.
ServletResponse - public int getBufferSize()
Returns the actual buffer size used for the response.
If no buffering is used, this method returns 0.
1
2
3
응답에 사용될 버퍼의 실제 크기를 반환한다.
버퍼가 사용되지 않는다면 0을 반환한다.
ServletResponse - public void flushBuffer()
Forces any content in the buffer to be written to the client.
A call to this method automatically commits the response, meaning the status code and headers will be written.
1
2
3
버퍼의 모든 내용이 클라이언트에 보내질 수 있도록 커밋한다.
즉, 응답 내용과 상태 코드와 헤더가 작성된다.
ServletResponse - public void resetBuffer()
Clears the content of the underlying buffer in the response without clearing headers or status code.
If the response has been committed, this method throws an IllegalStateException.
1
헤더나 상태 코드를 지우지 않고 응답에서 기본 버퍼의 내용을 지운다.
ServletResponse - public boolean isCommitted()
Returns a boolean indicating if the response has been committed.
A committed response has already had its status code and headers written.
1
응답이 커밋되었는지 여부를 나타낸다.
ServletResponse - public void reset()
Clears any data that exists in the buffer as well as the status code and headers.
If the response has been committed, this method throws an IllegalStateException.
1
2
3
버퍼에 있는 모든 데이터와 상태 코드 및 헤더를 지운다.
이미 응답이 커밋되었으면, 예외를 던진다.
ServletResponse - public void setLocale(Locale loc)
Sets the locale of the response, if the response has not been committed yet.
It also sets the response’s character encoding appropriately for the locale, if the character encoding has not been explicitly set using setContentType or setCharacterEncoding, getWriter hasn’t been called yet, and the response hasn’t been committed yet.
If the deployment descriptor contains a locale-encoding-mapping-list element, and that element provides a mapping for the given locale, that mapping is used.
Otherwise, the mapping from locale to character encoding is container dependent.
This method may be called repeatedly to change locale and character encoding.
The method has no effect if called after the response has been committed.
It does not set the response’s character encoding if it is called after setContentType has been called with a charset specification, after setCharacterEncoding has been called, after getWriter has been called, or after the response has been committed.
Containers must communicate the locale and the character encoding used for the servlet response’s writer to the client if the protocol provides a way for doing so.
In the case of HTTP, the locale is communicated via the Content-Language header, the character encoding as part of the Content-Type header for text media types. Note that the character encoding cannot be communicated via HTTP headers if the servlet does not specify a content type;
however, it is still used to encode text written via the servlet response’s writer.
1
2
3
응답이 아직 커밋되지 않은 경우 응답의 지역(Locale) 을 설정한다.
HTTP의 경우 로케일은 텍스트 미디어 유형에 대한 Content-Type 헤더의 일부로 문자 인코딩인 Content-Language 헤더를 통해 전달된다.